How was the Asian Financial Crisis resolved?
Topic of Study [For H2 History Students]:
Paper 2: Economic Development after Independence
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme II Chapter 2: Asian Financial Crisis
An overview of the Crisis
In the early 1990s, many member nations of ASEAN pegged their exchange rates to the US dollar (USD). Given the dominant position of the Americans in the global economy, the peg instilled strong market confidence. Over time, the economic expansion in the region led to increased foreign capital inflows. By June 1997, cross-border flows in Southeast Asia totaled US$173 billion.
Greater access to capital had encouraged the provision of private loans. In turn, firms and household investors had ploughed funds into the real estate market. As a result, an asset bubble was formed. When the bubble burst, the Bank of Thailand declared its inability to prop up the largest finance company, Finance One, triggering fears of an impending market crash.
The anticipation of loan defaults resulted in the withdrawal of funds by short-term loan creditors. On the other hand, the gradual recovery of the Japanese economy resulted in the appreciation of the Yen and an interest rate hike. This led to shift of capital from Southeast Asia to Japan markets. The Bank of Thailand struggled to maintain the peg, such that nearly of its reserves were lost, forcing them to float the baht on 2 July 1997.
The unpegging of the Thai baht from the U.S. dollar in July 1997 and the baht’s subsequent collapse are commonly regarded as the triggers of the Asian crisis. The floating of the baht was made necessary by the exhaustion of Thai foreign exchange reserves, after months of futile efforts to stave off necessary policy adjustments and financial sector reforms. The crisis was preceded by an investment bubble, especially in real estate and stock markets, by widespread structural and prudential problems in the financial sector, and by a very rapid buildup of short-term foreign debt liabilities.
An excerpt from “The Asian Financial Crisis: Lessons for a Resilient Asia” by Wing Thye Woo, Jeffrey Sachs and Klaus Schwab.
Concerted efforts for crisis management
In view of the Asian Financial Crisis, governments in Southeast Asia sought solutions to dampen the adverse impacts. On 28 February 1998, finance ministers in ASEAN had gathered in Jakarta to set up a “mutual monitoring system. They agreed to seek technical support from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) to enhance the development of the system. Later, this system was known as the ASEAN Surveillance Process (ASP).
Ideally, the monitoring system will function as an early warning system, so that the affected member nations can intervene before the economic setback escalates into another crisis.
Before the Asian financial crisis, there were no surveillance mechanisms that functioned to detect irregularities in regional finance markets, either in ASEAN or in East Asia. In that respect, these two mechanisms were formed to address the same problem. However, while the ASEAN Surveillance Process oversees the ASEAN member states, the ASEAN+3 Surveillance Process addresses all East Asian countries.
An excerpt from “ASEAN as a Method: Re-centering Processes and Institutions in Contemporary Southeast Asian Regionalism” by Ceren Ergenç
ASEAN Plus Three: The Chiang Mai initiative
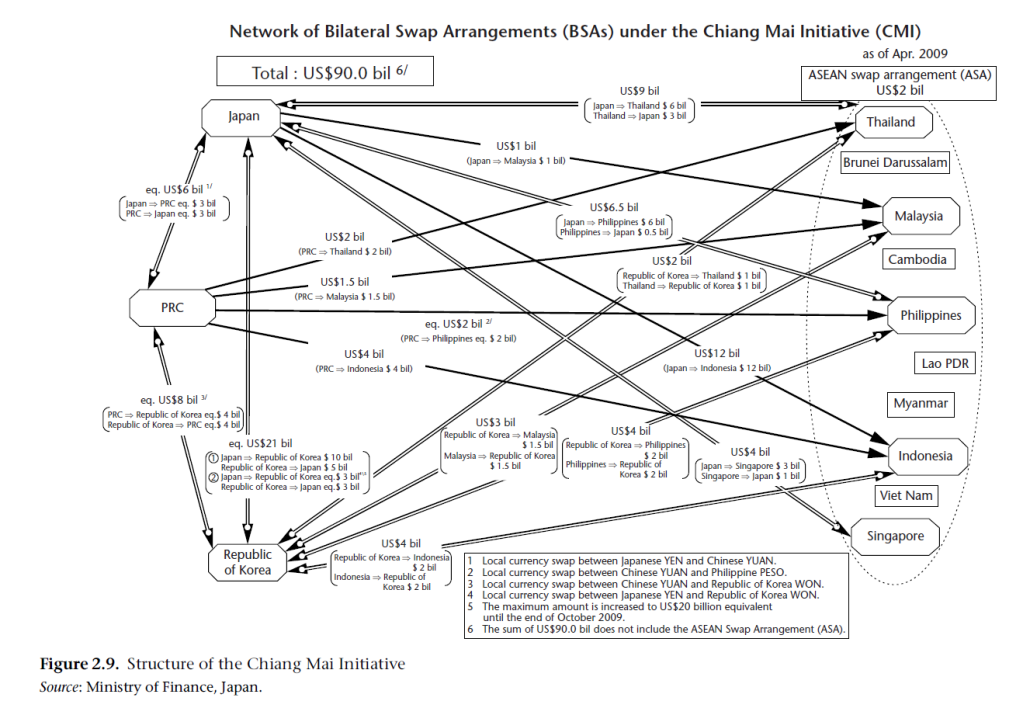
In 1999, the ASEAN Plus Three (APT) [or ASEAN+3] Summit was held, involving ASEAN members and three external powers – China, Japan and South Korea. In 6 May 2000, the APT met in Chiang Mai, Thailand, to derive a regional solution to avert another Asian Financial Crisis.
The Chiang Mai Initiative (CMI) became the first regional swap arrangement to address short-term liquidity difficulties in the Asia.
The CMI functioned on two branches:
- ASEAN Swap Arrangement (ASA) among the ASEAN member nations
- Bilateral Swap Arrangement (BSA) among ASEAN+3 countries
An important feature of the CMI was that crisis-affected members requesting short-term liquidity support could immediately obtain financial assistance up to an amount equivalent to 10 percent (later raised to 20 percent) of the maximum amount that could be borrowed, and that the remainder was to be provided to the requesting member under an IMF program. […] Essentially, the CMI was intended to be used for crisis lending and hence required conditionality.
An excerpt from “Monetary and Financial Cooperation in East Asia: The State of Affairs After the Global and European Crises” by Masahiro Kawai, Yung Chul Park and Charles Wyplosz.
In 2004, an expanded framework was proposed, known as the Chiang Mai Initiative Multilateralisation (CMIM). The CMIM would involve all ten members of ASEAN, China, Japan and South Korea, with a combined size of US$240 billion worth of foreign exchange reserves. Five years later, the CMIM was founded.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– How far do you agree that the responses to manage the Asian Financial Crisis were adequate and effective?
Join our JC History Tuition to recap on the Asian Financial Crisis topic. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.










