What are Special Economic Zones of China?
Topic of Study [For H2 History 9174 Students]:
Paper 1: The Development of the Global Economy (1945-2000)
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme II Chapter 2: Transformation of East Asian Economies (China, 1978-2000)
Vanguards and forerunners: Introducing the SEZs
Between 18 and 22 December 1978, the 3rd Plenary Session of the 11th Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party was held. During this session, the Chinese government began its pivotal journey in undergoing ambitious economic reforms to correct the errors of the Maoist economic system.
As part of Deng Xiaoping‘s economic reform that began in 1979, the government designated four Special Economic Zones (SEZs): Shenzhen (深圳), Zhuhai (珠海), Shantou (汕头) and Xiamen (厦门).
These SEZs were economically open areas that promoted technology transfer, foreign investment and export activities. China sought to harness its large pool of labour to produce labour-intensive goods for export. By doing so, it can accumulate foreign exchange earnings to meet the demands of its capital-starving economy.
In addition, SEZs were important in accessing foreign technology to stimulate growth. With the influx of foreign direct investment, these SEZs could then utilise foreign technology and production techniques to enhance the processes of domestic enterprises.
The designation of the above-mentioned four SEZs was intentional. Their locations were identified given their proximity to external economies, namely Taiwan, Macau and Hong Kong. There were contemplations of using these SEZs to integrate with these external economies that may eventually lead to ‘political reunification’. Besides, there was limited capital investment, thus the open-door policy could not be implemented nation-wide from the outset.
Case Study: Shenzhen
Among the four SEZs, Shenzhen became the largest and most successful zone (see Table 1.1). Its success could be attributed to its unique geographic location, given that it functioned as a channel between the mainland and Hong Kong. Furthermore, Shenzhen has abundant land resources that gave it much potential for industrial development.
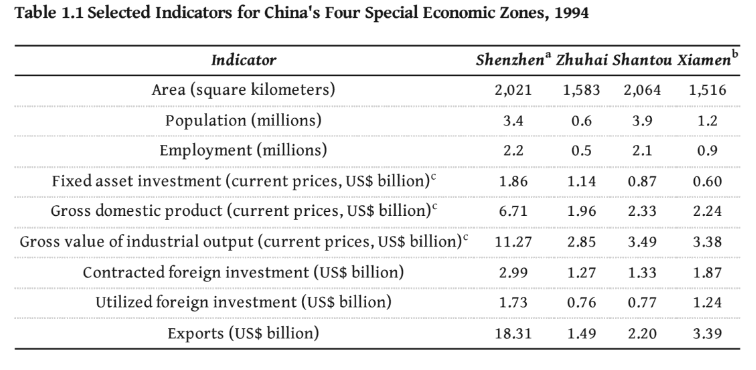
Three major work conferences were held to finetune the development strategies for Shenzhen (1981, 1985 and 1990). For example, the 1990 work conference emphasised the importance of the SEZs as the core of the coastal development strategy as well as the generation of foreign exchange. At that time, the central government directly supervised policymaking and appointments for Shenzhen.
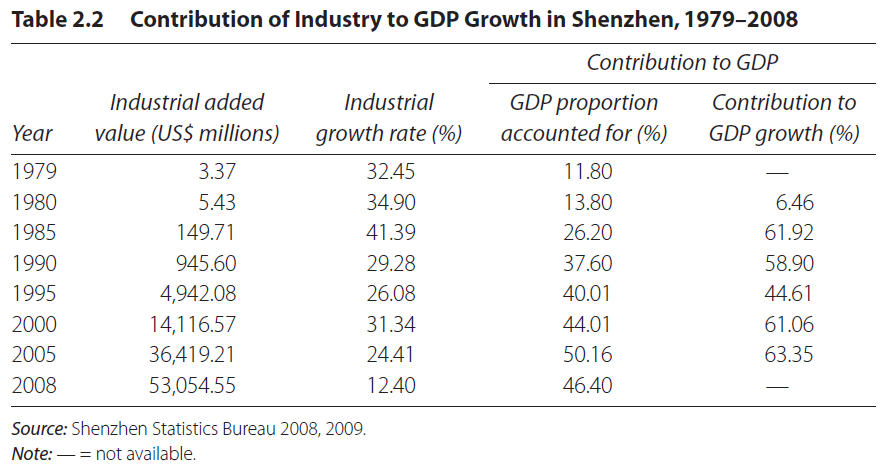
Since the 1990s, Shenzhen’s industrial growth contributed to half of the growth in Gross Domestic Product. In 1994, contribution by the industry was 43 percent compared 11.8 percent in 1979 (see Table 2.2).
In fact, Shenzhen has become one of the political battlefields between the reform and conservative factions in the central government. Its success or failure, at least in the early 1980s, would determine the fate of the reform. The SEZ promoters hoped to use Shenzhen not only to promote foreign investment and technology transfer, but also to learn how to adopt selected features of a market system into the socialist reform. Shenzhen, as well as other SEZs, represented in miniature the very essence of the new reforms.
An excerpt taken from “Pioneering Economic Reform in China’s Special Economic Zones: The Promotion of Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer in Shenzhen” by Weiping Wu.
In 1984, fourteen more coastal cities were designed as SEZs, such as Yantai (烟台), Tianjin (天津) and Shanghai (上海). These SEZs prioritised the promotion of foreign investment.
Join our JC History Tuition to learn more about the economic transformation of China and Japan under the theme of The Global Economy. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.








 https://pixabay.com/photos/gold-bars-wealth-finance-gold-bars-163519/
https://pixabay.com/photos/gold-bars-wealth-finance-gold-bars-163519/


