What is OPEC?
Topic of Study [For H2 History Students]:
Paper 1: Understanding the Global Economy (1945-2000)
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme II Chapter 1: Problems of economic liberalisation
History of the OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was formed in September 1960. Its five founding members comprised of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iran, Iraq and Venezuela. The OPEC was established with a central aim of price stabilization for oil producers through discussions.
Before OPEC, seven multinational corporations dominated the petroleum industry since the mid-1940s. They were commonly known as the “Seven Sisters”, which consisted of
- Anglo-Persian Oil Company [British Petroleum]
- Gulf Oil
- Standard Oil for California [Chevron]
- Texaco
- Royal Dutch Shell
- Standard Oil Company for New Jersey [Exxon]
- Standard Oil Company for New York [Mobil]
Ever since its establishment, the OPEC membership continued to grow (such as Algeria, Nigeria, Ecuador and Gabon). As of 2019, the OPEC has 14 members.
The “Black Gold”: Energy Crisis of the 1970s
In 1973, the OPEC members reduced oil output and caused a spike in the oil prices. Its consequences were devastating to many oil-dependent economies since it is an essential resource for industrialization. In 1979, the oil price surged extensively in the wake of the Iranian Revolution. By 1980, global oil price had peaked over US$35 per barrel.
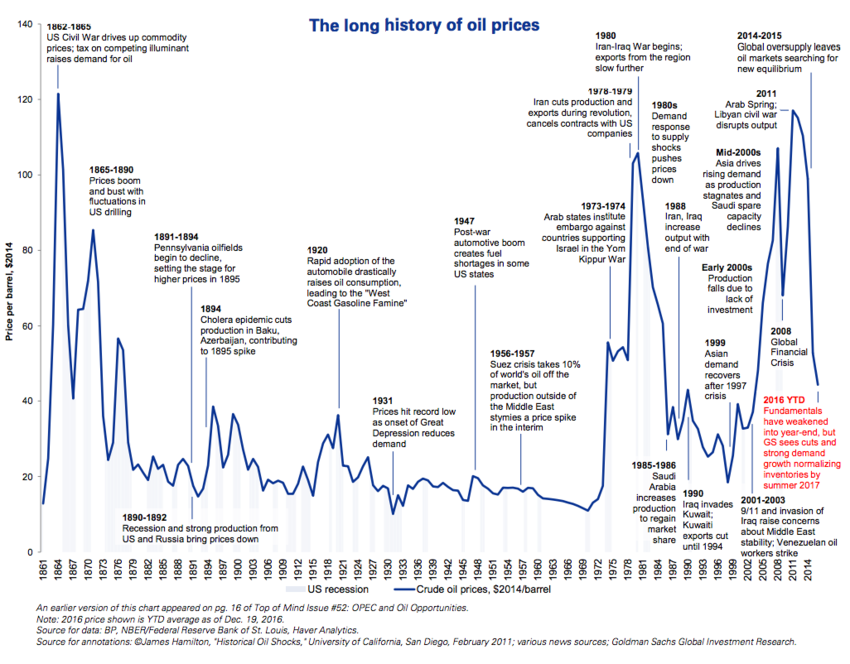
[Chart taken from the World Economic Forum]
Even the economic giant, USA, was not spared from this unilateral action by the OPEC. The unprecedented impacts included stagflation (high inflation rates and economic stagnation) that forced households to conserve oil consumption for the first time in U.S. history.
Petrodollar Recycling
OPEC members benefited tremendously from this oil spike. With the increased in earning from oil exports (also known as ‘petrodollars’), these oil exporters engaged in petrodollar recycling, in which their money was loaned to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Then, the IMF used these loans to finance the balance of payment deficits by oil-importing countries.
However, these non-oil exporting countries were disadvantaged, especially for the Latin American nations in the 1970s. Over time, these borrowing nations had growing debts that later gave rise to the Third World Debt Crisis in the 1980s.
The Oil Glut of 1986
By mid-1980s, some countries had reduced their dependence on oil to sustain economic development. For instance, advanced economies like USA and France explored alternative energy. Likewise, Japanese auto firms engaged in innovation to produce fuel-efficient automobiles. These developments led to the falling demand for oil in the global petroleum industry.
On the other hand, there were emerging oil producers that did not belong to the OPEC that engaged in oil extraction. In 1980, the Canadian Government introduced the National Energy Program to promote self-sufficiency for oil. As such, the increase in supply from these alternative sources had diminished the share of the OPEC members.
OPEC went for a last-ditch attempt to maintain high oil prices by decreasing oil production from 1980 to 1986. However, these efforts were unsuccessful. In 1986, oil price plunged from $27 to nearly above $10 per barrel.
Recent Developments
In view of the COVID-2019, the decreased economic activities (such as airline flights) led to the fall in demand for oil. OPEC has held online meetings to contemplate on the decrease in oil production. However, some countries are hesitant to follow through as Saudi Arabia takes the lead.
On 20 April 2020, the US crude oil (West Texas intermediate crude, WTI) plunged from US$17.85 a barrel to negative US$37.63 a barrel. This is a typical scenario in which oil glut combined with falling demand results in falling oil prices, such that there is negative crude oil price.
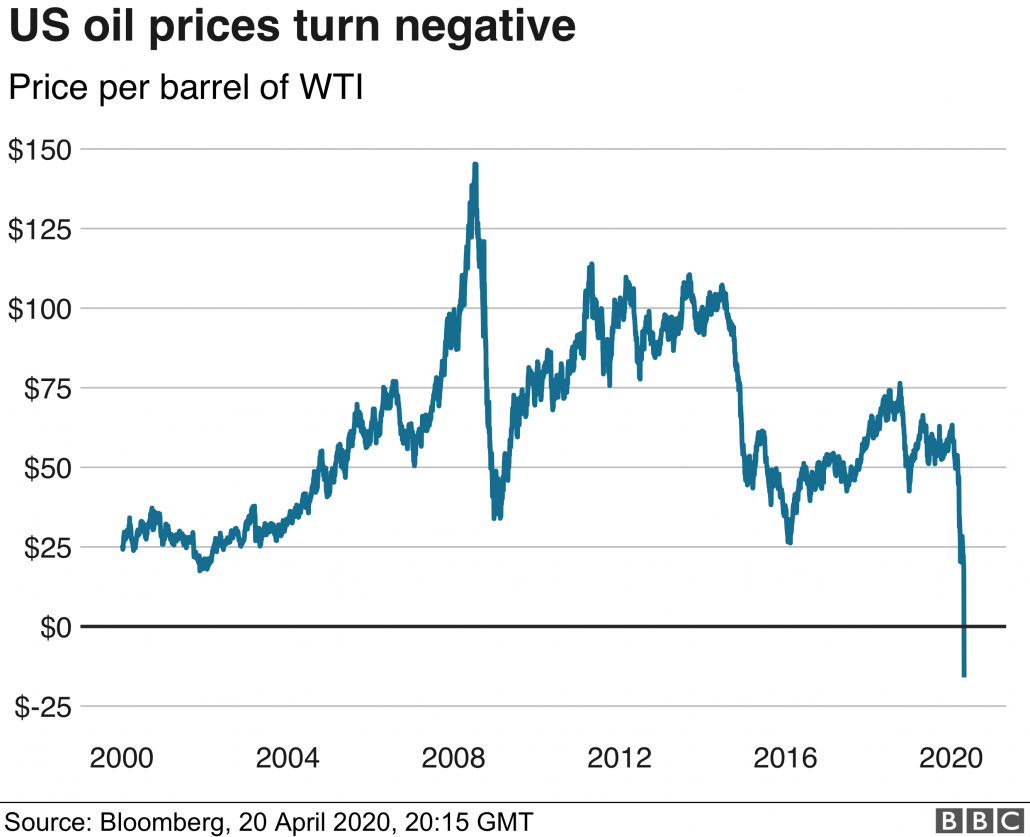
[Published on BBC; Source: Bloomberg]
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– Assess the economic impacts of volatile oil prices in affecting the development of the global economy from 1945 to 2000 [to be discussed in class].
Join our JC History Tuition and learn how to organise your learning materials to do well for the essay writing component at the A Level examination. Our online lessons feature content discussion and class practices to review knowledge application.
The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.











