An Agenda for Peace
Topic of Study [For H2 History Students]:
Paper 1: Safeguarding International Peace and Security
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme III Chapter 2: Political Effectiveness of the UN in maintaining international peace and security
The report
In 1992, the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali submitted a report titled “An Agenda for Peace: Preventive diplomacy, peacemaking and peace-keeping“. Earlier, the Security Council requested the Secretariat to assess the strengths and limitations of peacekeeping.
Changing context: New challenges
In the post-Cold War world, the circumstances have changed. Boutros-Ghali outlined these shifts in his report:
In the course of the past few years the immense ideological barrier that for decades gave rise to distrust and hostility and the terrible tools of destruction that were their inseparable companions has collapsed.
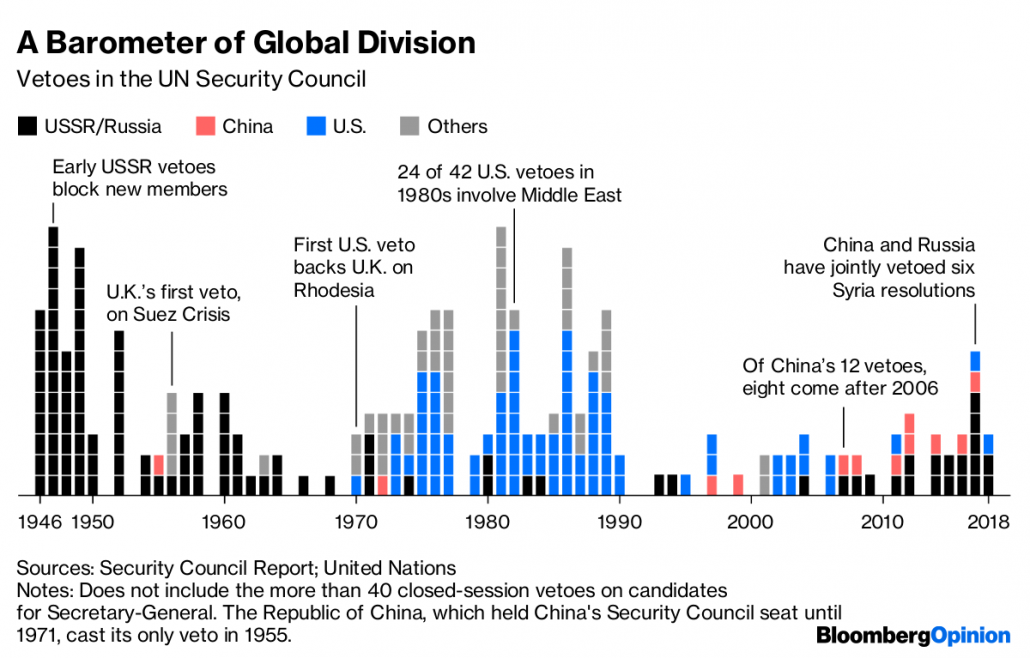
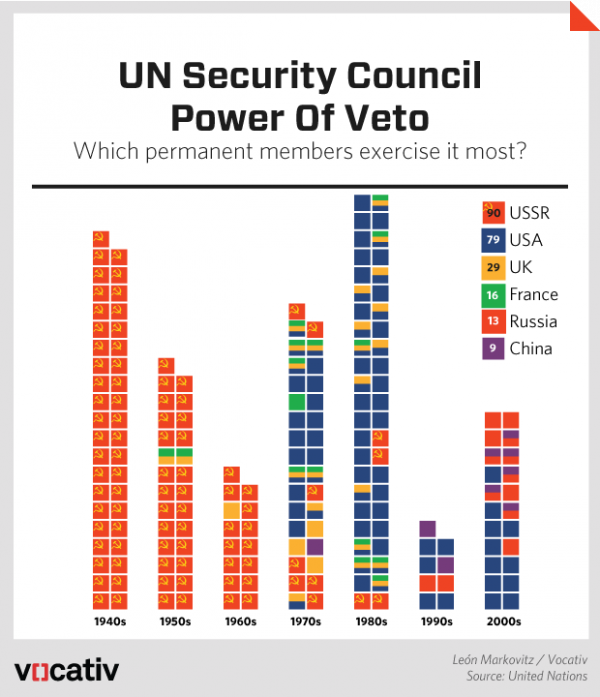
… With the end of the cold war there have been no such vetoes since 31 May 1990, and demands on the United Nations have surged. Its security arm, once disabled by circumstances it was not created or equipped to control, has emerged as a central instrument for the prevention and resolution of conflicts and for the preservation of peace.
An excerpt from “An Agenda for Peace” report, 17 June 1992.
In view of the changing global context, the Secretary-General proposed a few key concepts, such as preventive diplomacy and peace-making.
Preventive diplomacy
In other words, the United Nations should intervene through the conduct of diplomacy before conflicts break out or escalate. This course of action can be undertaken by the Secretary-General, Security Council or General Assembly.
Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali established six regional divisions within the consolidated Department for Political Affairs whose principal task was to gather and analyze information to assist him in preventing conflicts.
… between March and December 1992, the Department for Political Affairs had undertaken thirty-one missions to various trouble spots on the initiative either of the Secteray-General or a member state.
An excerpt from “Preventive Diplomacy at the UN” by Bertrand G. Ramcharan.
Preventive diplomacy was achieved through efforts like confidence-building measures, fact-finding and the use of early warning systems. Its application was observed in the above-mentioned missions in potential conflict zones like Moldova, Haiti and Tajikistan.
Peacemaking
In addition to preventive diplomacy, the report also proposed peacemaking. As stated in the report, the United Nations bear the “responsibility to try to bring hostile parties to agreement by peaceful means”. Such efforts are carried out with reference to Chapter VI of the United Nations Charter (Pacific Settlement of Disputes).
In practice, peacemaking was carried out in response to the conflicts in Cambodia and Somalia. The United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) was supported by Yasushi Akashi, Special Representative in Cambodia, who combined the application of peacekeeping and peacemaking to oversee civil administration, demobilisation and disarmament of military factions.
However, the successes of peacemaking were limited in Somalia. The escalation of the civil war gave rise to casualties that resulted in eventual departure of the United Nations Operation in Somalia II (UNOSOM).
UN/US intervention in the civil war, initiated in December 1992 and entered into with high hopes both of saving millions from starvation and restoring peace and stability to the country, ending ignominiously in the killing first of 25 Pakistani peacekeepers on 6th June 1993, and then of 18 American Rangers in October 1993. President Clinton soon announced that US troops would be withdrawn from Somalia and the complete withdrawal of UN peacekeeping troops had been effected by March 1995, with few of the mandate objectives of UNOSOM II achieved.
An excerpt from “Peacekeeping and Peacemaking: Towards Effective Intervention in Post-Cold War Conflicts” by Tom Woodhouse, Robert Bruce and Malcolm Dando.
Funding issues
Lastly, the report described how peacekeeping operations during the Cold War were hampered by arrears that amounted to over $800 million. Between 1945 and 1987, 13 peacekeeping operations were established. These operations have cost nearly $8.3 billion in total. As such, Boutros-Ghali raised the suggestion for member nations for “their peace-keeping contributions to be financed from defence, rather than foreign affairs”.
The Secretary-General made three proposals to address the finance issue. The following is one of the proposals.
Proposal three: This suggested the establishment of a United Nations Peace Endowment Fund, with an initial target of $1 billion. The Fund would be created by a combination of assessed and voluntary contributions, with the latter being sought from Governments, the private sector as well as individuals. Once the Fund reached its target level, the proceeds from the investment of its principal would be used to finance the initial costs of authorized peace-keeping operations, other conflict resolution measures and related activities
An excerpt from “An Agenda for Peace” report, 17 June 1992.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– Assess the effectiveness of the UN reforms in maintain the relevance of the organisation in maintaining international peace and security in the post-Cold War era?
Join our JC History Tuition to reinforce your comprehension of historical concepts and apply them to your essay and source based case study questions. Our online learning programmes feature thematic revision and skills development workshops to prepare you for the GCE A Level History examinations.
The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.