What was Dag Hammarskjöld’s Summary Study?
Topic of Study [For H1/H2 History Students]:
Paper 1: Safeguarding International Peace and Security
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme III Chapter 2: Political Effectiveness of the UN in maintaining international peace and security
Historical context
Following the outbreak of the Suez Canal Crisis in 1956, the United Nations Secretary-General (UNSG) Dag Hammarskjöld deployed the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) to supervise the “cessation of hostilities” involving the armed forces of France, Israel and the United Kingdom, as well as to “serve as a buffer between the Egyptian and Israeli forces”.
The Summary Study
On 9 October 1958, Hammarskjöld submitted to the General Assembly a report known as the “Summary Study of the Experience Derived from the Establishment of the United Nations Emergency Force“.
Also known more commonly as the “Summary Study” in short, the UNSG reported his reflections on the pioneer peacekeeping mission. His purpose was to institutionalise peacekeeping at the international level.
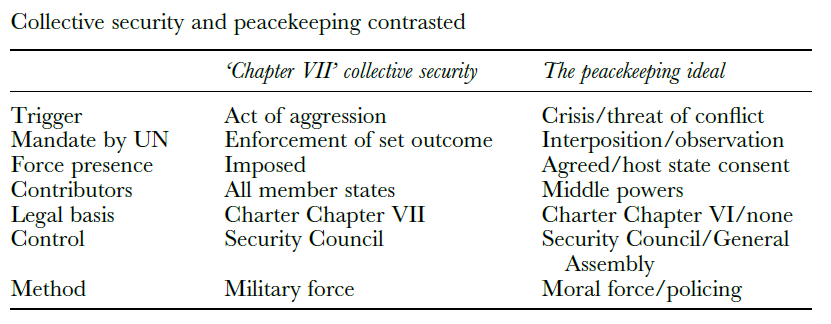
At the outset of the Summary Study, Hammarskjöld noted that peacekeeping did not involve ‘the type of force envisaged under Chapter VII of the Charter’. Without this legal base, the activity had to be an elective one.
There were two senses to this. First, there could be no deployment on a state’s territory ‘without the consent of the Government concerned’. Second, it followed that if Chapter VII was not to be used as the basis of a peacekeeping action then Article 43, with its obligations on member states to ‘make available to the Security Council, on its call’ whatever military forces were deemed necessary, could not be invoked. They could only be freely offered by contributing states in response to a request from the UN. These principles would ‘naturally hold valid for all similar operations in the future’.
An excerpt from “Peacekeeping and the International System” by Norrie MacQueen.
As described by MacQueen, the UNSG had envisaged peacekeeping as a concept that required consent from the host-state. Also, operational support to form the peacekeeping force had to be carried out on a voluntary basis. The second requirement proved to be costly and problematic later on, as observed in the United Nations Mission in Congo (ONUC).
In his Summary study, the Secretary-General held, with regard to the principle of freedom of movement, that an agreement as to what should be considered an area of operations of the force would be needed in future operations.
[…] In the Congo operation (1960-1964), secessionist movements exercised control from time to time over large tracts of the Congolese territory. The Secretary-General was therefore more or less forced to negotiate with those movements rather than use force to enter the territory. The UN also concluded cease-fire agreements with forces not under the control of the central Congolese government.
An excerpt from “Protection of Personnel in Peace Operations: The Role of the ‘Safety Convention’ against the Background of General International Law” by Ola Engdahl.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– Assess the view the the United Nations Secretary-Generals have played a vital role in the maintenance of international peace and security.
Join our JC History Tuition to recap on the United Nations topic. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.